Unveiling The Nigerian Police Ranks: A Comprehensive Guide
The Nigeria Police Force (NPF) stands as the principal law enforcement and lead security agency in Nigeria, a nation officially known as the Federal Republic of Nigeria, situated on the western coast of Africa. Understanding the intricate structure of the NPF, particularly the various Nigerian Police Ranks, is crucial for anyone interested in law enforcement, public service, or simply the operational dynamics of one of Africa's most populous nations. This detailed exploration will shed light on the hierarchy, responsibilities, and the path to a career within this vital institution.
From its foundational history to its modern-day constitutional mandate, the NPF operates under a clear, hierarchical system designed to ensure order, discipline, and effective command. As of 2024, the structure of Nigerian Police Ranks continues to define roles, responsibilities, and powers at every level, reflecting the regimental nature essential for maintaining peace and security across Nigeria's diverse geography and multiethnic society. This article provides an in-depth look at the 16 distinct ranks, their symbols, and the broader context of the force's operations.
Table of Contents
- A Brief History of the Nigeria Police Force
- The Hierarchical Structure: Understanding Nigerian Police Ranks
- Symbols and Insignia: Visualizing Authority
- Salary and Pension Framework: Rewarding Service
- Pathways to a Career in the NPF
- The NPF's Role in a Diverse Nation
- Conclusion: Upholding Law and Order
A Brief History of the Nigeria Police Force
The origins of the Nigeria Police Force can be traced back to a remarkably early period, making it a very old organization. Records indicate that the force was founded in 1820, long before Nigeria gained its independence. Initially, these were localized constabularies, often established by colonial authorities to maintain order in specific regions. As the British colonial influence expanded, so did the need for a unified policing body. A significant milestone in the evolution of policing in Nigeria occurred in 1930 when the various regional forces were consolidated, and the unified police force officially became known as the Nigeria Police Force (NPF). This marked a pivotal moment, laying the groundwork for the national police structure that exists today. Following Nigeria's independence in 1960 and its transition to a republic in 1963, the NPF continued to evolve, adapting to the needs of a sovereign nation. The 1999 Nigerian Constitution formally designated the NPF as the national police of Nigeria, solidifying its role as the primary law enforcement agency. This historical trajectory underscores the NPF's deep roots and its continuous adaptation to serve a nation with nearly 200 million inhabitants, making it the most populated country in both West Africa and the entire continent.The Hierarchical Structure: Understanding Nigerian Police Ranks
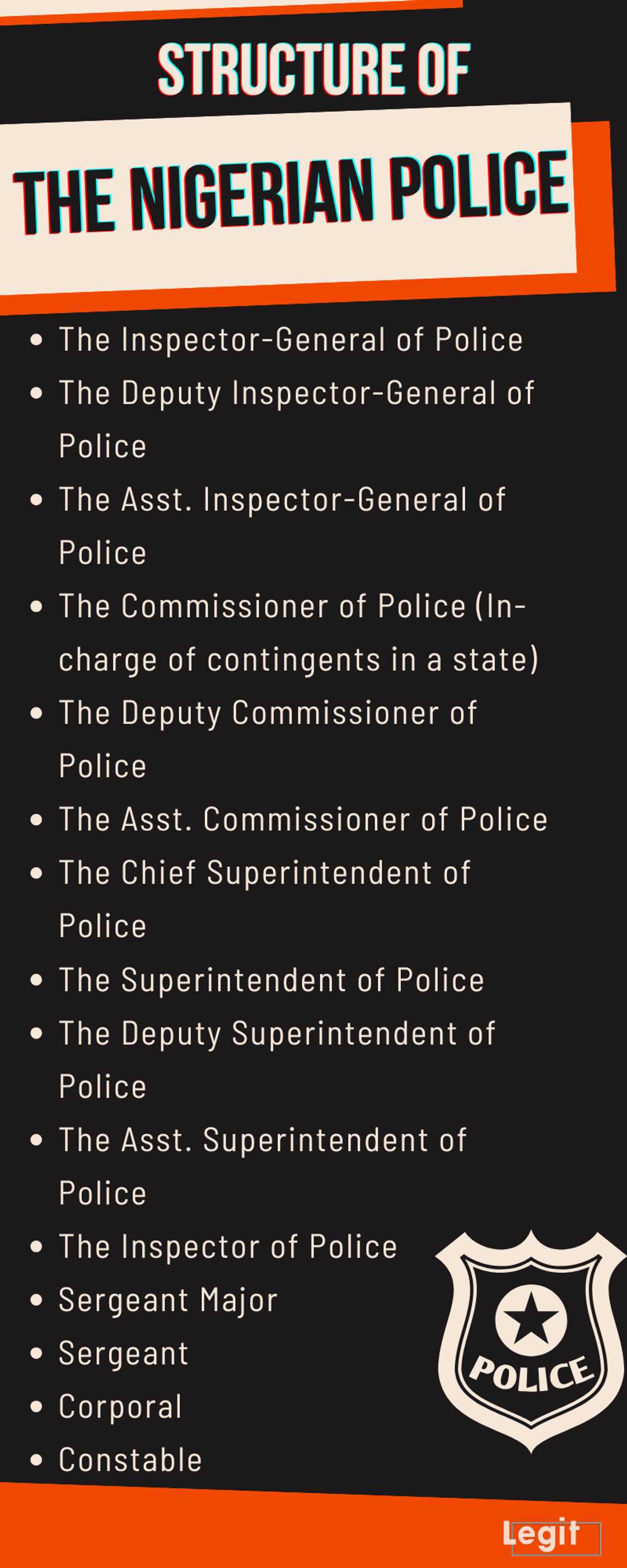
The Nigeria Police Force operates under a rigid hierarchical structure, where each of the Nigerian Police Ranks signifies a specific level of authority, responsibility, and expertise. This clear chain of command is fundamental to the force's operational efficiency, ensuring that directives are followed and accountability is maintained. The force has ranks that span from the lowest entry point, the Recruit Constable, all the way up to the highest position, the Inspector General of Police. This article will provide information on the list of the 16 Nigerian Police Ranks and their symbols, offering a comprehensive overview of this essential framework. Let's explore these ranks in ascending order, providing clarity on the command structure.Senior Officers: Command and Leadership
These ranks represent the strategic and executive leadership of the NPF, responsible for policy formulation, command of large formations, and overall direction of the force. 1. **Inspector General of Police (IGP):** This is the highest rank in the Nigeria Police Force. The IGP is the head of the NPF and is responsible for its overall administration and operational control. The position holds immense power and influence, overseeing all police activities across the nation. 2. **Deputy Inspector General of Police (DIG):** Directly below the IGP, Deputy Inspector Generals assist the Inspector General in various capacities, often heading specific departments or directorates within the Force Headquarters. 3. **Assistant Inspector General of Police (AIG):** AIGs typically command Police Zonal Commands, which comprise several state commands. They are crucial in coordinating operations across larger geographical areas. 4. **Commissioner of Police (CP):** The Commissioner of Police is the highest-ranking officer in charge of a State Police Command. They are responsible for maintaining law and order within their respective states, overseeing all police operations and personnel. The "first person to have the highest rank in all the police is Commissioner General," which might refer to an early equivalent or a specific historical context of this rank's significance. 5. **Deputy Commissioner of Police (DCP):** DCPs serve as deputies to the Commissioner of Police in state commands, often heading specific departments within the state command or overseeing major operational divisions. 6. **Assistant Commissioner of Police (ACP):** Assistant Commissioners of Police typically head Area Commands within a state, supervising several Divisional Police Officers (DPOs). They play a vital role in bridging the gap between state command headquarters and local police divisions. This is a high rank in the armed forces, and it is the fourth highest Nigeria Police Rank, as indicated in the provided data. This implies that the Assistant Commissioner of Police holds significant authority and is a crucial part of the senior leadership.Intermediate Ranks: The Backbone of Operations
These ranks form the operational core of the NPF, directly managing and supervising frontline officers and executing police duties at the divisional and station levels. 7. **Chief Superintendent of Police (CSP):** CSPs often serve as Divisional Police Officers (DPOs), commanding police divisions. They are responsible for all police activities within their division, including crime prevention, investigation, and public order maintenance. This Nigerian Police Rank is higher than the rank of Assistant Superintendent. 8. **Superintendent of Police (SP):** Superintendents assist CSPs in managing divisions or head specialized units within a division or command. 9. **Deputy Superintendent of Police (DSP):** DSPs are typically in charge of police stations or specific sections within a division. They are directly involved in day-to-day police operations and supervision of junior officers. 10. **Assistant Superintendent of Police (ASP):** ASPs are often fresh graduates from police academies, serving as entry-level commissioned officers. They are assigned to various duties, including leading patrols, supervising junior ranks, and conducting preliminary investigations. 11. **Inspector of Police (IP):** Inspectors are non-commissioned officers who play a crucial role in supervising and leading junior ranks. They often head police posts or specialized sections within a station.Junior Ranks: Frontline Law Enforcement
These ranks constitute the majority of the police force, directly engaging with the public, responding to incidents, and carrying out the fundamental duties of law enforcement. 12. **Sergeant Major:** A senior non-commissioned officer, often responsible for administrative duties and discipline within a unit or station. 13. **Sergeant:** Sergeants are experienced officers who supervise constables and are often in charge of small teams or specific duties like traffic control or patrol supervision. 14. **Corporal:** Corporals are junior non-commissioned officers, often leading small teams of constables or performing specialized tasks. 15. **Constable:** Constables are the entry-level uniformed police officers. They are the frontline responders, responsible for general police duties, including patrol, crowd control, and assisting in investigations. 16. **Recruit Constable:** This is the initial rank for individuals undergoing training at police academies. They are not yet fully fledged officers but are in the process of becoming one. The Recruit Constable is a rank in the Nigerian Police that signifies the beginning of a career in law enforcement.Symbols and Insignia: Visualizing Authority
Just like numerous police, military, and paramilitary agencies worldwide, the Nigerian Police Ranks, symbols, and command structures are well laid out. Each rank is visually represented by specific insignia worn on the uniform, making the hierarchy immediately apparent. These symbols typically include stars (pip), Nigerian coats of arms, and other emblems, which are clearly defined and recognized throughout the force. For instance, the Inspector General of Police would wear a unique combination of symbols that clearly distinguish them as the head of the force, while a Constable would wear simpler insignia, reflecting their entry-level position. These visual cues are essential for maintaining discipline, recognizing authority, and ensuring smooth operations within the NPF.Salary and Pension Framework: Rewarding Service
The remuneration for each position within the Nigeria Police Force reflects the responsibilities and degrees of expertise associated with that rank. The Nigerian Police Force salary is divided into grades and steps, based on ranks or distinctions among officers on the same level. Generally, higher ranks command higher salaries, commensurate with the increased duties, leadership roles, and strategic importance they hold. Beyond active service, the NPF also provides a robust pension framework. The Nigerian Police Force’s rank structure reflects a clear hierarchy of responsibilities, and its pension framework offers financial security to officers after active service. This system is designed to provide a stable future for officers who dedicate their lives to public service, recognizing their commitment and the inherent risks of their profession. These provisions are crucial for attracting and retaining skilled personnel within the force, ensuring that officers can look forward to a secure retirement.Pathways to a Career in the NPF
For individuals aspiring to start a career in the Nigerian Police as a policeman or policewoman, understanding the various Nigerian Police Ranks and the different departments and units is the first crucial step. The NPF offers diverse career paths, from general duty policing to specialized units such as the Mobile Police Force (MOPOL), Criminal Investigation Department (CID), Special Anti-Robbery Squad (SARS - now defunct, but illustrates the concept of specialized units), and various administrative roles. Entry into the NPF typically begins at the Constable or Assistant Superintendent of Police (for graduates) levels, followed by a structured promotion system based on performance, experience, further training, and availability of vacancies. The force emphasizes continuous professional development, providing opportunities for officers to enhance their skills and progress through the ranks, contributing to the overall effectiveness and professionalism of the Nigerian Police Force.The NPF's Role in a Diverse Nation
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa, situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It is a multiethnic country with a diverse geography, with climates ranging from arid to humid equatorial. This vast and varied landscape, coupled with its multiethnic population, presents unique challenges for law enforcement. The Nigeria Police Force is the principal law enforcement and the lead security agency in Nigeria, tasked with maintaining peace and order across this complex nation.Constitutional Mandate and Responsibilities
The legal foundation of the NPF is enshrined in the nation's supreme law. Section 214 of the 1999 Nigerian Constitution explicitly states: "There shall be a police force for Nigeria, which shall be known as the Nigeria Police Force, and subject to the provision of..." This constitutional backing underscores the NPF's crucial role in the governance and security architecture of Nigeria. Its responsibilities are broad, encompassing crime prevention, detection, investigation, apprehension of offenders, maintenance of public order, and enforcement of laws and regulations. The NPF also plays a significant role in internal security operations, often collaborating with other security agencies.The NPF in a Global Context
While primarily focused on domestic security, the Nigeria Police Force also operates within a broader international context. Nigeria, as a prominent nation in Africa, often engages in regional and international peacekeeping missions. The NPF's structure and operations, including its Nigerian Police Ranks, are often benchmarked against international policing standards, though adapted to the local context. The force faces various challenges, including issues of public trust, resource constraints, and the evolving nature of crime, including money laundering as evidenced by recent news involving a "Nigerian senator's wife in money laundering mess as UK." Despite these challenges, the NPF remains a critical pillar of stability in Nigeria, working to uphold the rule of law and protect its citizens.Conclusion: Upholding Law and Order
So, there you have it on the Nigerian Police Ranks and salaries. This comprehensive overview has detailed the 16 distinct ranks within the Nigeria Police Force, from the Recruit Constable to the Inspector General of Police, highlighting their respective responsibilities, the hierarchical structure, and the significance of each position. We've explored the historical evolution of the NPF, its constitutional mandate, and the framework that governs its operations, including the remuneration and pension schemes that provide financial security to officers. Understanding the intricacies of the Nigerian Police Ranks is not just about knowing titles; it's about appreciating the complex system that underpins law enforcement in a dynamic and diverse nation. The NPF's commitment to maintaining peace and order is paramount for the stability and development of Nigeria. What are your thoughts on the structure and roles within the Nigeria Police Force? Do you have any questions about specific ranks or the NPF's operations? Share your insights in the comments below! If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this detailed insight into Nigeria's primary law enforcement agency. Stay tuned for more updates and in-depth analyses on critical topics concerning Nigeria and its institutions.
Nigerian police ranks, symbols, duties and salaries 2022 - Legit.ng
Nigerian police ranks, symbols, duties and salaries (updated) - Legit.ng
![[Latest!] Nigerian Police Ranks and Their Symbols - Oasdom](https://www.oasdom.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/Oasdom.com-Nigeria-police-station-and-zones.jpg)
[Latest!] Nigerian Police Ranks and Their Symbols - Oasdom