Unlocking Wellness: The Power Of Vitamin C Wholistic Research
In the vast landscape of human health, vitamins stand as silent, yet indispensable, guardians of our well-being. These organic compounds, required in small quantities, orchestrate a symphony of metabolic functions crucial for growth, vitality, and overall optimal performance. Among them, Vitamin C holds a particularly prominent and fascinating position, often at the forefront of discussions surrounding immunity, longevity, and comprehensive health. This article delves into the profound world of Vitamin C Wholistic Research, exploring how a comprehensive, interconnected approach to this vital nutrient can unlock a deeper understanding of its unparalleled benefits.
From the intricate dance of cellular reactions to the macroscopic resilience of our immune system, Vitamin C is a cornerstone. While many understand its basic role in fending off colds, modern scientific inquiry, particularly through a "wholistic" lens, reveals a far more expansive and integrated influence on our health. We will explore how understanding Vitamin C not just as a single molecule, but as part of a larger nutritional ecosystem, offers a more potent pathway to wellness.
Table of Contents
- What Are Vitamins? The Building Blocks of Life
- Vitamin C: A Unique and Essential Player
- The Essence of Wholistic Research: A Paradigm Shift
- Natural Sources: The Wholistic Advantage of Vitamin C
- Beyond Immunity: The Broad Spectrum of Vitamin C's Benefits
- Scientific Insights into Wholistic Vitamin C Research
- Optimizing Vitamin C Intake: A Wholistic Approach
- The Future of Wholistic Vitamin C Exploration
- Conclusion: Embracing the Wholistic Path to Wellness
What Are Vitamins? The Building Blocks of Life
To truly appreciate the significance of Vitamin C Wholistic Research, it's essential to first grasp the fundamental role of vitamins themselves. Vitamins are organic molecules—or a set of closely related molecules called vitamers—that are essential to an organism in small quantities for proper metabolic function. They are distinct in several ways from other nutrients, primarily because they are organic compounds, meaning they’re made by animals and plants. This is why eating certain vegetables, meats, and other natural sources is crucial for obtaining them.
These tiny substances, found in the foods we eat, are not produced in sufficient quantities by our bodies, if at all. This means they must be derived from our diet. There are 13 essential vitamins, each playing a unique and critical role. They are needed for functions such as growth, metabolism, and nervous system activities. Vitamins are usually designated by selected letters of the alphabet, as in Vitamin D or Vitamin C, though they are also designated by chemical names, such as niacin and folic acid. Unlike minerals, which come from the soil and water, vitamins are made by plants and animals, highlighting the importance of a diverse diet.
Vitamin C: A Unique and Essential Player
Among the 13 vital vitamins, Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, stands out for several reasons. It is one of the water-soluble vitamins, meaning it dissolves in water and is not stored in the body in large amounts. This necessitates a regular intake through diet. What makes Vitamin C particularly intriguing from a biological standpoint is its variability across species. For example, Vitamin C can be synthesized by some species but not by others. Humans, along with a few other primates, guinea pigs, and some birds, lack the enzyme necessary to synthesize Vitamin C internally. This is why it is not considered a vitamin in the first instance for species that can produce it, but it is in the second for those, like us, who cannot. This biological quirk underscores its absolute essentiality in the human diet.
This vitamin plays a role in more than 100 different reactions in your body, making its influence incredibly widespread. From collagen synthesis, which is vital for healthy skin, bones, and blood vessels, to its potent antioxidant capabilities, Vitamin C is a workhorse. Its involvement in so many fundamental processes makes it a prime candidate for "wholistic research," which seeks to understand its broader impact rather than just isolated effects.
The Essence of Wholistic Research: A Paradigm Shift
The term "wholistic research" in the context of vitamins, and specifically Vitamin C Wholistic Research, signifies a shift from reductionist science to a more integrated understanding. Traditionally, scientific studies often isolate a single nutrient or compound to observe its effects on a specific bodily function. While valuable, this approach can sometimes miss the complex interplay between nutrients, the food matrix they come in, and the myriad of biochemical pathways they influence simultaneously.
Wholistic research, conversely, seeks to understand how Vitamin C functions within the entire biological system, considering its interactions with other vitamins, minerals, enzymes, and even gut microbiome. It acknowledges that the human body is an intricate network where no single component acts in isolation. This approach moves beyond simply identifying a deficiency or a single benefit, aiming instead to map out the cascading effects of optimal Vitamin C levels on overall health, resilience, and disease prevention. It asks not just "what does Vitamin C do?" but "how does Vitamin C contribute to a state of complete well-being, considering all its interactions?"
Natural Sources: The Wholistic Advantage of Vitamin C
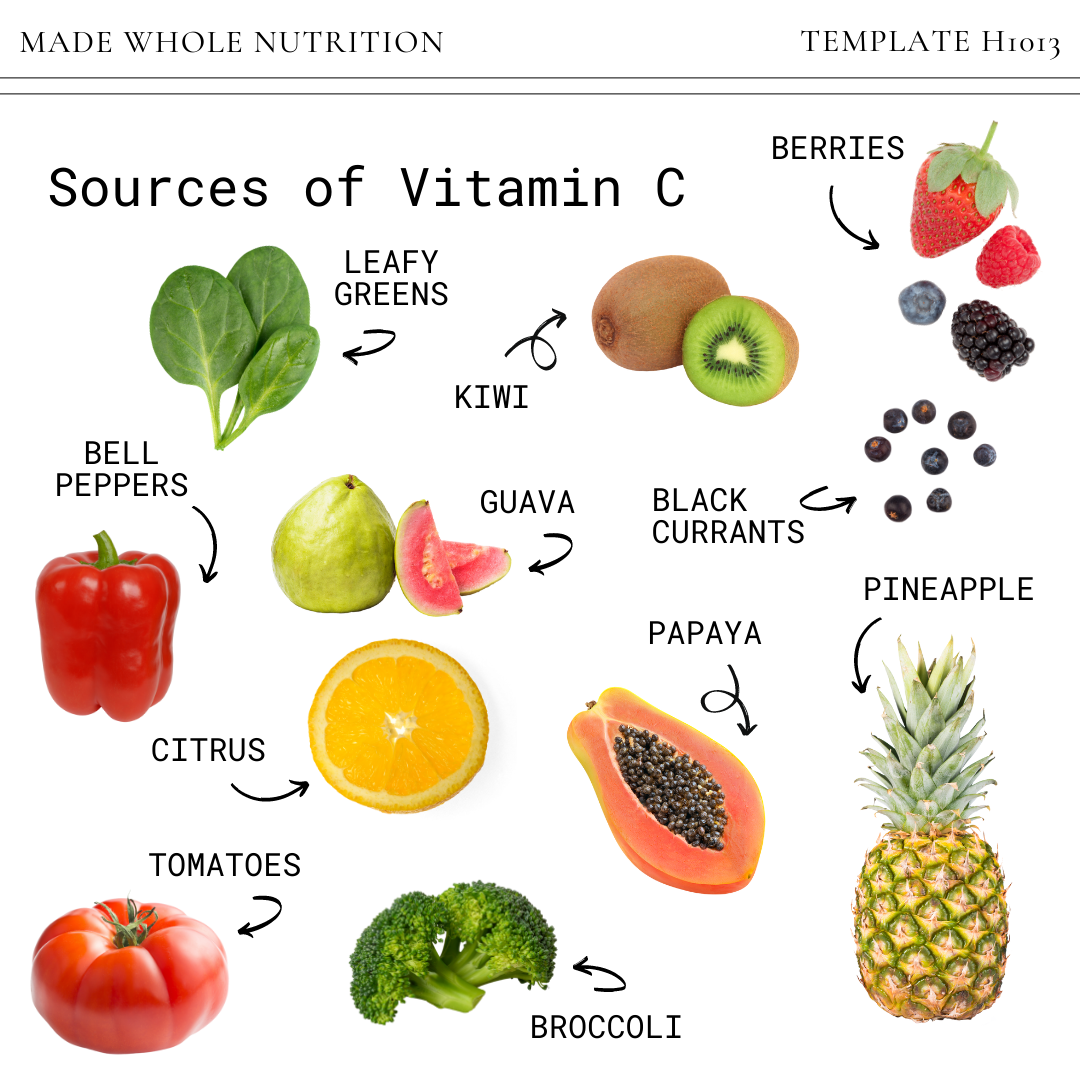
A cornerstone of any wholistic approach to nutrition is the emphasis on whole foods. Vitamins are nutrients that are found in the foods we eat, and for Vitamin C, this is particularly true. While synthetic supplements exist and can be beneficial, Vitamin C Wholistic Research often highlights the superior benefits of obtaining this vitamin from natural, food-based sources. Rich sources of Vitamin C include a wide array of fruits and vegetables, such as citrus fruits, berries, bell peppers, kiwi, and leafy greens.
The Synergy of Whole Foods
When we consume Vitamin C through whole foods, we are not just getting ascorbic acid; we are also ingesting a complex array of other beneficial compounds. These include bioflavonoids, carotenoids, and other phytonutrients that naturally occur alongside Vitamin C. Wholistic research suggests that these co-factors may enhance Vitamin C's absorption, utilization, and overall effectiveness in the body. This synergistic effect is often referred to as the "entourage effect," where the sum is greater than its individual parts. For instance, the antioxidants in a whole orange work together in ways that isolated ascorbic acid might not replicate entirely. This perspective aligns perfectly with the idea that vitamins are tiny substances found in the food we eat, and they’re organic compounds, meaning they’re made by animals and plants. This is why eating certain vegetables, meats and other natural sources is crucial for obtaining them, reinforcing the wholistic view.
Beyond Immunity: The Broad Spectrum of Vitamin C's Benefits
While Vitamin C is famously known for its role in supporting the immune system, the depth of Vitamin C Wholistic Research reveals a much broader spectrum of benefits. This vitamin plays a role in more than 100 different reactions in your body, influencing systems far beyond just fighting off infections. Its diverse functions contribute significantly to overall health and vitality, embodying the very essence of a wholistic nutrient.
Metabolism and Nervous System Support
Vitamins are needed for functions such as growth, metabolism, and nervous system activities, and Vitamin C is no exception. It is crucial for the biosynthesis of collagen, L-carnitine, and certain neurotransmitters. Collagen, a primary component of connective tissue, is essential for wound healing, healthy skin, bones, and blood vessels. L-carnitine is vital for energy production, transporting fatty acids into the mitochondria. Furthermore, Vitamin C acts as a co-factor in the production of neurotransmitters like norepinephrine, which impacts mood and cognitive function. This highlights its integral role in the body's fundamental processes, ensuring that our bodies require it in small quantities to function optimally.
Antioxidant Power and Cellular Protection
One of Vitamin C's most celebrated roles, and a key area of Vitamin C Wholistic Research, is its powerful antioxidant capacity. It helps prevent damage to cells and tissues by neutralizing harmful free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is implicated in the development of chronic diseases, including heart conditions, certain cancers, and neurodegenerative disorders, as well as the aging process. By protecting cells from this damage, Vitamin C contributes to cellular integrity and overall disease prevention, aligning with the idea that a balanced diet can prevent fatigue and other health issues like anemia or heart conditions.
Scientific Insights into Wholistic Vitamin C Research
The scientific community continues to explore the multifaceted roles of Vitamin C, with a growing emphasis on wholistic perspectives. Research methodologies are evolving to capture the intricate web of interactions that Vitamin C participates in. For instance, studies are looking at how Vitamin C levels correlate with overall health markers, not just specific disease outcomes. This involves examining its impact on inflammation, gut health, mental well-being, and even genetic expression, painting a more complete picture of its influence.
Understanding Complex Interactions
Wholistic research into Vitamin C also investigates its interplay with other micronutrients. For example, Vitamin C enhances the absorption of non-heme iron (iron from plant sources), which is crucial for preventing iron-deficiency anemia. It also works synergistically with Vitamin E, regenerating Vitamin E after it has neutralized free radicals, thereby extending its antioxidant activity. This demonstrates that vitamins and minerals are micronutrients required by the body to carry out a range of normal functions. However, these micronutrients are not produced in our bodies and must be derived from external sources, making their combined intake and interaction a focal point of wholistic study.
Furthermore, some research has shown that Vitamin B6 may help protect the body in various ways, and while distinct from Vitamin C, this highlights the broader concept that different vitamins contribute to a robust defense system. For example, Biotin is naturally present in some foods, such as salmon and eggs, and just like Vitamin C, it contributes to overall metabolic health. The interconnectedness of these nutrients is a central theme in Vitamin C Wholistic Research.
Optimizing Vitamin C Intake: A Wholistic Approach
Given Vitamin C's essentiality and broad impact, optimizing its intake is a key component of a wholistic health strategy. The most effective way to ensure adequate Vitamin C levels is through a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables. As discussed, the synergy of whole foods provides not just Vitamin C but also a host of other beneficial compounds that enhance its efficacy. This approach aligns with the understanding that vitamins are substances that your body needs to grow and develop normally, and they are found in many foods as well as dietary supplements.
While supplements can play a role, especially in cases of dietary insufficiency or increased need, the wholistic perspective prioritizes food-first strategies. Many vitamin deficiencies can contribute to fatigue (extreme tiredness), and a balanced diet can prevent fatigue and other health issues like anemia or heart conditions. This applies directly to Vitamin C, as prolonged deficiency can lead to scurvy, a severe condition. Therefore, making diverse, Vitamin C-rich foods a regular part of your diet is a simple yet powerful step towards comprehensive well-being. This includes a variety of green leafy, orange, and yellow vegetables such as carrots and spinach (rich sources of Vitamin A, but also often co-occurring with Vitamin C in a balanced diet), ensuring a broad spectrum of nutrients.
The Future of Wholistic Vitamin C Exploration
The field of Vitamin C Wholistic Research is dynamic and continually evolving. Future studies are likely to leverage advanced technologies to map out even more intricate biochemical pathways and gene-nutrient interactions. There's a growing interest in personalized nutrition, where dietary recommendations, including Vitamin C intake, are tailored based on an individual's genetic makeup, lifestyle, and health status. This will further refine our understanding of optimal Vitamin C levels for different individuals and life stages.
Moreover, research will continue to explore the role of Vitamin C in emerging areas like epigenetics (how diet can influence gene expression), its potential in managing chronic inflammatory conditions, and its contribution to mental health and cognitive resilience. As our understanding deepens, the wholistic view of Vitamin C will become even more central, moving beyond simple supplementation to an integrated strategy that maximizes its natural potential within the body's complex systems. The emphasis will remain on how these organic compounds that our bodies require in small quantities truly help us to function optimally and are essential for a wide range of bodily processes, including metabolism and overall health.
Conclusion: Embracing the Wholistic Path to Wellness
In conclusion, Vitamin C is far more than just an immune booster; it is a foundational nutrient deeply intertwined with countless bodily functions. The paradigm of Vitamin C Wholistic Research offers a profound and comprehensive lens through which to understand its true power. By acknowledging its complex interactions with other nutrients, its natural synergy within whole foods, and its widespread impact on metabolism, cellular protection, and overall vitality, we move towards a more enlightened approach to health.
Embracing a wholistic perspective means recognizing that our bodies are intricate ecosystems, and the nutrients we consume contribute to a delicate balance. Prioritizing a diverse, nutrient-rich diet, abundant in natural Vitamin C sources, is not merely about preventing deficiencies but about fostering optimal health and resilience. We encourage you to explore the myriad ways Vitamin C, as part of a balanced lifestyle, can elevate your well-being. What are your favorite Vitamin C-rich foods? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, or explore our other articles on essential nutrients and holistic living!

Vitamin C: Nootropic Benefits Uses Dosage & Side Effects
Vitamin C Foods List

DHC Vitamin C ดีเอชซี วิตามินซี รับประทาน 60 วัน บรรจุ 120 แคปซูล ล๊อต